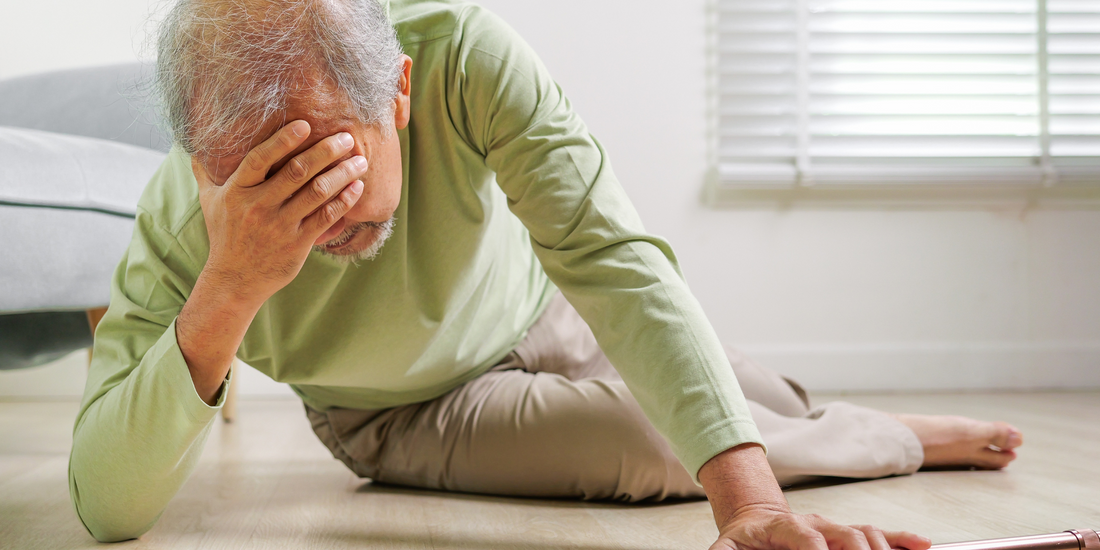
When the floor disappears under your feet: how falls can change life
Falls are one of the most common causes of accidents worldwide and are a serious health risk. They are particularly dangerous for older people, but younger people are also not preserved. The consequences of a fall can be far -reaching and devastating, from slight bruises to serious injuries such as broken bones or head trauma. In addition to the physical damage, a fall can also have profound psychological effects, since the fear of further falling often leads to a restriction of mobility and quality of life.
In this comprehensive contribution, we will analyze the causes of falls, present current statistics and discuss detailed prevention measures in order to effectively minimize the risk of falling.

Global statistics on the risk of falling
Falls are an important global health problem. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) die about every year 646,000 people Due to fall -related injuries. This number illustrates the scope of the problem because falls are among the most common causes of accidents -related deaths. Older people are particularly affected because the risk of falling increases with age. Approximately 37.3 million falls Medical treatment worldwide require medical treatment annually, which emphasizes the need to take preventive measures.
In Germany the numbers are also alarming. Surve out every year 5 million people a fall, and round 30% of the over 65 year olds fall at least once a year. This number increases significantly in humans over the age of 80, since almost every second in this age group has a fall annually. According to the Federal Statistical Office If every tenth fall leads to such serious injuries that hospital treatment is required.
Causes of falls: a detailed overview
Falls are often the result of a combination of internal and external risk factors. A comprehensive understanding of these causes is crucial for the development of effective prevention strategies.
Internal risk factors
- Physical restrictions: With increasing age, muscle strength and coordination decreases. Muscle mass and strength decrease significantly in old age, which affects the ability to stabilize and balance. This can lead to an increased risk of falls and injuries.
- Chronic diseases: Diseases like arthritis, osteoporosis, Parkinson's or diabetes influence the risk of falling significantly. Arthritis causes joint pain and stiffness, which restricts mobility. Osteoporosis leads to an increased fragility of the bones, which reinforces the severity of the injuries in the event of falls. Parkinson's affects the movement coordination and balance, while diabetes increases the risk of peripheral neuropathy, which in turn influences the risk of falling.
- Taking medication: Many older people occupy several medication, what as Polyphaharmacy is known. Medicines such as blood pressure lowerers, sedatives or pain relievers can cause dizziness, drowsiness or slow ability to react. A British study has shown that taking more than four medication by the risk of falling up to 50% increased. Interactions between different drugs can also increase the risk.
- Bad eyesight: A reduced eyesight is a significant risk factor for falls. People with visual impairments often have difficulty recognizing obstacles on their way. Regular eye examinations and wearing suitable visual aids are therefore crucial for fall prevention.
External risk factors
- Slippery soils and stumbling blocks: In the home, smooth floors, especially in wet rooms such as bathrooms or kitchens, as well as loose carpets and cables are frequent stumbling blocks. An investigation of the Robert Koch Institute showed that about 60% of the falls Complete in your own apartment, often due to such environmental conditions. The risk of falling on slippery surfaces can be reduced by using non -slip mats and securing carpets.
- Bad lighting: Inadequate lighting is another important risk factor. Dark corridors, insufficiently illuminated stairs and other poorly illuminated areas increase the risk not to recognize obstacles in time. Motion detectors or additional lighting in critical areas can help here.
- Unsuitable footwear: Shoes without a firm hold or with smooth soles also contribute to the risk of falling. Older people in particular should make sure to wear stable -fitting shoes with non -slip soles. Shoes with good damping properties and non -slip soles can significantly reduce the risk of falling.
- Outdoor environmental conditions: Weather conditions such as rain, snow or ice can increase the fall risk outdoors. It is therefore important to be particularly careful in adverse weather conditions and, if necessary, use stray agents on sidewalks.
Consequences of falls: Effects on body and psyche
The consequences of a fall are not only physical nature, but can also have profound psychological effects. The severity of the consequences often depends on the type of fall and general health of the data subject.
Physical consequences
- Broken bones: Hip fractures are one of the most common and most serious consequences of a fall. In Germany, for example 100,000 people A hip fracture. The severity of the injury is alarming: about 20-30% Those affected die from the direct or indirect consequences of the fracture within one year. Hip fractions often lead to permanent need for care or restricted mobility.
- Head injuries: Falls can also cause severe head injuries, especially in people who take blood -thinning medication. These injuries are often difficult to diagnose and can lead to long -term neurological damage. An investigation of the National Institutes of Health (Nih) showed that about 10% of the fall -related head injuries can lead to long -term disabilities.
- Sprains and bruises: Even less serious injuries such as sprains or bruises can be considerably painful and affect mobility. Especially in older people whose bone structure is already weakened, even slight injuries can have serious effects.
Psychological consequences
- Fear of falling: After a fall, many people develop strong fear of further falls. This so -called Fear of falling Can cause those affected to restrict their freedom of movement, which in turn leads to muscle reduction and a further deterioration in balance. Approximately 50% of peoplewho have already experienced a fall suffer from this fear of falling. The fear of another fall can significantly impair the quality of life and lead to social isolation.
- Depression and social isolation: The effects of a fall can also cause mental illnesses such as depression. People who are restricted after a fall in their mobility often tend to social isolation, which increases the risk of depression. Studies show that people who suffer from chronic diseases and lose their mobility due to falling have a higher risk of depressive symptoms.

Prevention strategies: Measures to reduce the risk of fall
Prevention of falls requires a comprehensive understanding of the risk factors and the implementation of targeted measures. Here are some of the most important strategies for reducing the fall risk:
Adjustment of the living environment
- Secure carpets and floor coverings: Loose carpets should be attached or removed with non -slip documents to avoid stumbling blocks. In bathrooms and kitchens, non -slip mats should be used to reduce the risk of slipping on wet floors. The use of anti-slip coatings on smooth floors can also be helpful.
- Improve lighting: Sufficient lighting in all areas of the house is crucial. Lighter lamps should be installed, especially in corridors, stairwells and bathrooms. Motion detectors and night lights can offer additional security, especially at night or with a limited perspective.
- Clear cables and objects: Cable, toys and other loose objects should be cleared out regularly to avoid stumbling blocks. A decent and tidy living environment significantly reduces the risk of falls.
- Barrier -free bathroom: Handles should be installed in the bathroom on the toilet and bathtub. A non -slip shower mat can reduce the risk of slips while showering. The installation of a floor -like shower can also help minimize the risk of falling.
Strengthen physical fitness and balance
- Regular movement: Regular physical training, especially strength and balance exercises, can significantly reduce the risk of falling. Studies show that targeted training programs are the risk of falls to up to 45% can lower. Exercises like Tai Chi and Balance training have proven to be particularly effective because they improve coordination and balance.
- Fall prevention programs: Participation in special fall prevention programs can also be helpful. Programs like "Stepping on" or "A Matter of Balance" offer targeted exercises and information on fall prevention and can significantly reduce the risk of falling in older adults.
- Health monitoring: Regular health checks for monitoring diseases and the effect of medication are important. Checking the visual capacity and adaptation of glasses or contact lenses can also contribute to fall prevention. A helpful tool set in practice Emergency bracelet The advantages are that the bracelet is on the wrist and is triggered by automatic creation.
Improvement of mobility and safety outdoors
- Wear suitable footwear: Wearing stable, well -fitting shoes with non -slip soles can significantly reduce the risk of falling outdoors. Especially in winter conditions, shoes with good grip should be used to minimize the risk of slips on smooth or icy paths.
- Non -slip measures outdoors: For snow or ice, sidewalks should be cleared and scattered regularly. In many cities there are scattering services that ensure safe sidewalks in winter. In winter conditions you should go particularly carefully and, if necessary, use support materials such as walking sticks.
- Use aids: In the event of uncertainties when walking, aids such as walking aids or walkers can be useful and emergency bracelets are helpful if there is a fall. These devices offer additional stability and support, especially for people with limited mobility or balance.

First aid measures in the event of a fall: act correctly immediately
When you come across someone who has fallen, quickly and carefully act is crucial. Falls can lead to various types of injuries, from light bruises to serious breaks or head injuries. The following measures are important to properly provide the injured and avoid further damage until professional medical help arrives. Therefore always recommend you one First aid Equipment nearby.
Immediate measures in the event of a fall
1. Preserve rest and check security
- Check the environment: Before you approach the injured, make sure that the environment is safe and there are no further dangers. If necessary, switch off electrical devices, clear stumbling blocks and ensure sufficient lighting if necessary.
2. Contact contact
- Talk to the injured person: Try carefully to address the injured to find out whether he is consciousness and moves. A simple "How do you feel?" Or "Can you hear me?" Is enough. This helps you to better assess the person's condition.
3. Do not move unless it is absolutely necessary
- Ensure stability: If the injured is conscious, ask him not to move unless it is absolutely necessary (e.g. if it is in direct danger, as on a section of the street). Movements can make existing injuries worse.
4. Check for unconsciousness and breathing
- Consciousness and respiratory control: Check whether the injured person is conscious and breathes normally. If the injured is passed out, but breathes, carefully put it in the stable side position to keep the airways free. If there is no breathing, start with the heart-lung resuscitation (HLW) until help arrives.
5. Ensure a pleasant position
- positioning: If the injured person is conscious and no serious injuries such as broken bones or head injuries have occurred, you can carefully bring it into a comfortable position that minimizes pain and inconvenience. Make sure that he does not violate himself
A holistic approach to fall prevention
Falls are a serious health problem that can have far -reaching physical and psychological consequences. Prevention requires a holistic approach that takes into account both internal and external risk factors. By adapting the living environment, the improvement of physical fitness and the implementation of targeted security measures outdoors, the risk of falling can be significantly reduced and the quality of life of those affected can be improved.
It is crucial that both individuals as well as communities and health institutions take extensive measures for fall prevention. Education, education and regular health check are key components of a successful prevention program. By working together to reduce the fall risk, we can significantly improve the security and quality of life for people of all ages.